What is it?
Some Distributed Computing applications implement decentralized Architecture Patterns, in which different nodes need to agree among themselves. This problem can be solved using the Byzantine agreement method.
How does it work?
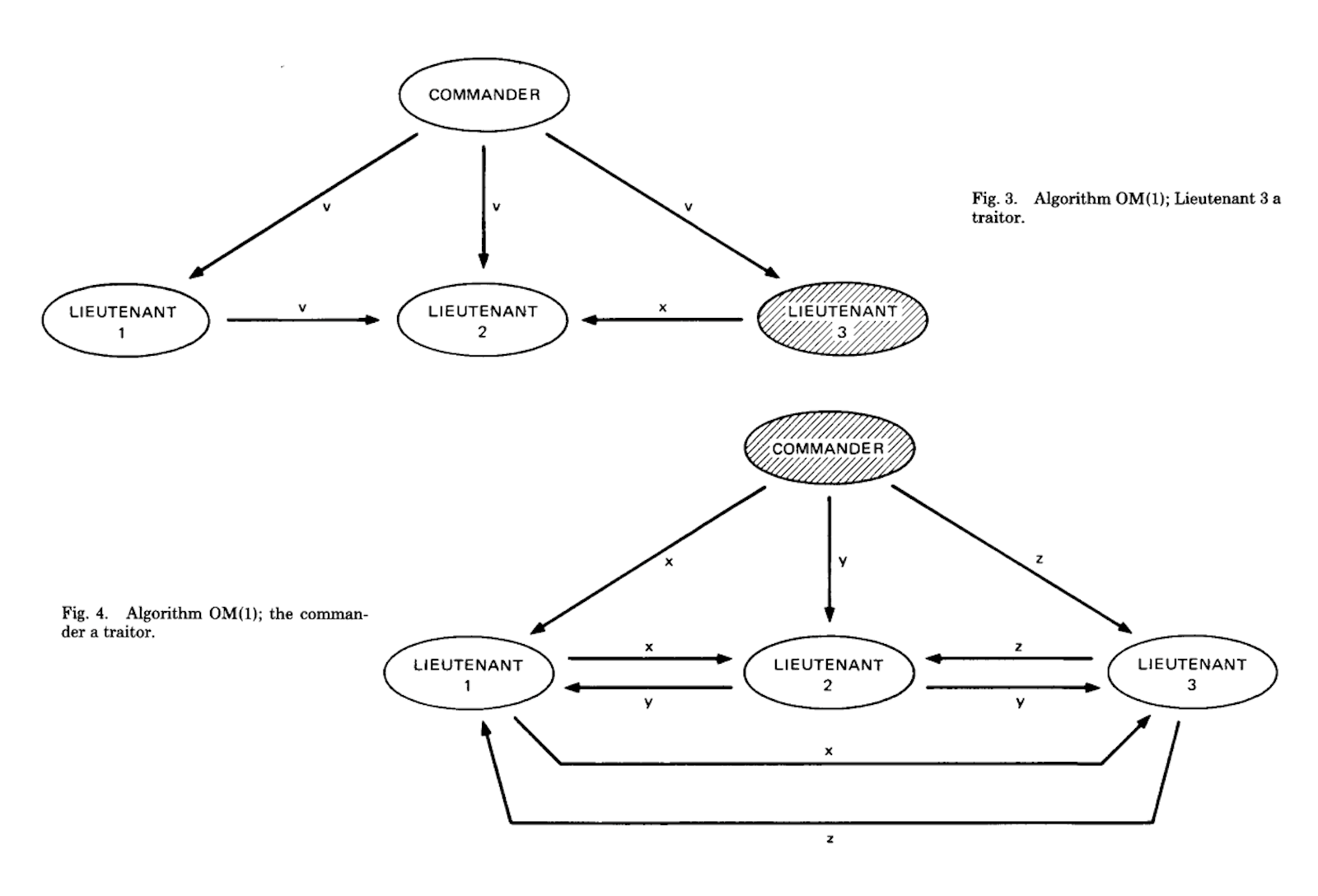
It’s said that during the crusades, the Byzantine general wanted to individually attack or retreat. However, if a partial attack or a partial retreat would to occur, it would compromise Byzantine forces. It was vital that all generals followed the same instruction. To make things worse, each general was far away from each other, which also compromises the reliability of the information. Under each general, we also have lieutenants. Either the general may be malicious and issue different orders to each lieutenant, or lieutenants may be malicious and choose not to follow the major’s order.
Generals and lieutenants are just analogies for computer nodes. Leslie Lamport et al., proposes that for malicious nodes, reliable nodes are needed to ensure the data is not compromised and decisions are taken as it should.