What is it?
A decentralized architecture refers to systems in which control and data are distributed across nodes, not controlled from a single master node, which increases expansion potential, Load Balancing and fault tolerance. Applications like blockchain and Peer-to-peer networks work as decentralized architectures.
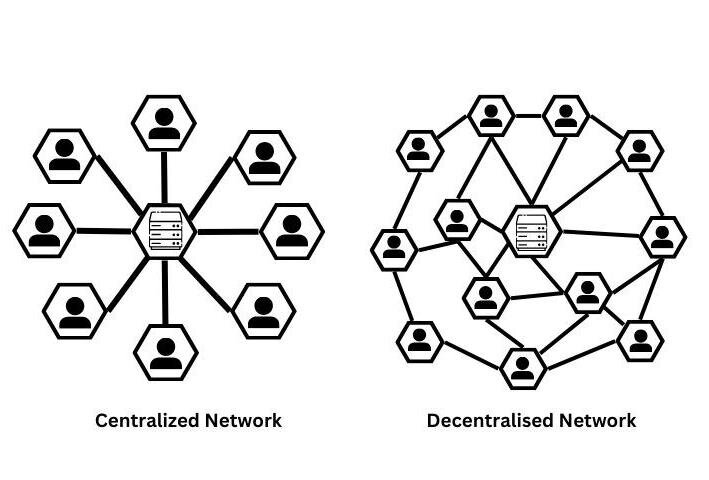
How does it work?
Each node of a decentralized network must have the similar rules as the others. As no central node is taking decisions, consensus must be reached between different nodes to solve problems, confirm transactions and share data. However, we need to assume that some nodes may be faulty, down or are malicious, which in this case, we cannot trust every single node. In these cases, strategies like Byzantine Agreement and Proof of Work methods are used to determine the decision to take.