Connections in Apache Airflow are used for storing credentials and parameters used for connecting with external services.
They can be defined as environment variables in the Airflow Docker image, or inside the Web Server, using the user interface.
A list of all managed connections can be found in the official documentation.
Creating connections in Airflow
This is the interface for listing all defined connections:
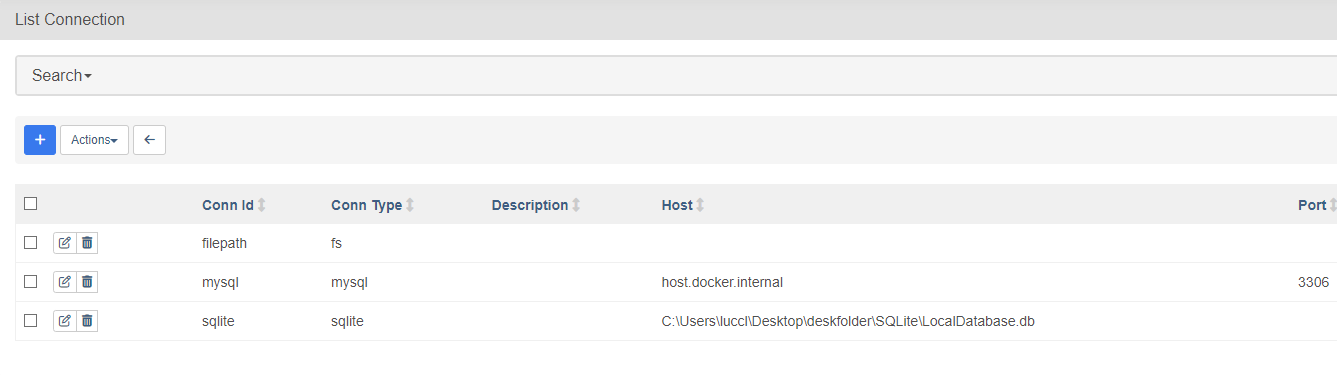
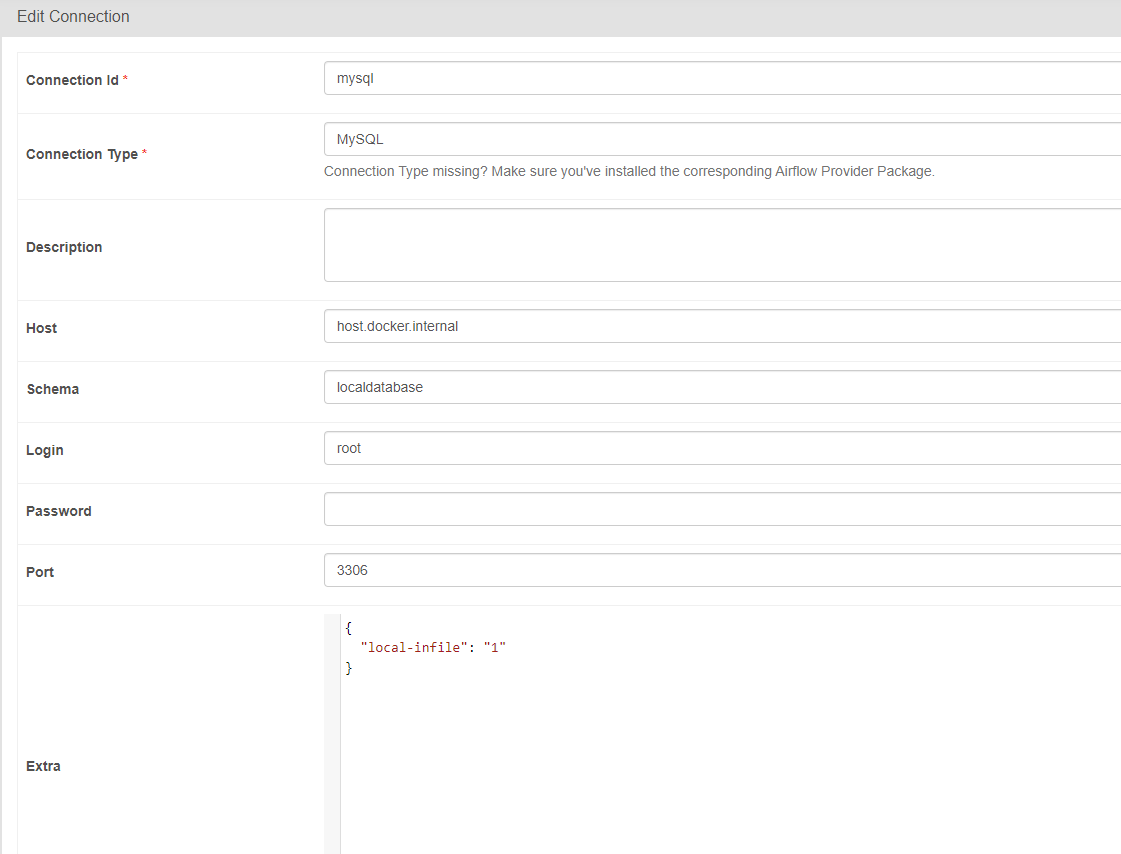
Let’s delve deeper into the MySQL connection, for example. Here, we can define the ID, which will be used inside the DAG for referencing the connection. Other information are dependent on the Connection Type. This could be referring to database or API credentials, URLs, and other specific information.
Referencing connections in DAG
To reference the connection in Python code, just use the same connection ID defined in the Web Server in the DAG or Operator parameters.
# Task-based reference
task = MySqlOperator(
task_id="dummy_task",
sql="SELECT * FROM table",
mysql_conn_id="mysql") # Specifying the connection defined in Airflow
# DAG-based reference using default arguments.
default_args = {
"owner": "lucas",
"start_date": datetime(2024, 2, 25),
"mysql_conn_id": "mysql", # Specifying the connection defined in Airflow
}
with DAG(
dag_id="dummy_dag",
schedule_interval=None,
default_args=default_args,
catchup=False,
) as dag:
pass