A CSS property determine the style of an element using CSS. It has various different properties, referring to position, border, text, color, and so on.
Coloring
CSS can be specified using defined names, RGB values, HEX values, and HSL values.
List of standardized color names
All browsers support a list of 140 colors, each defined by its own name. You can access the list clicking here.
RGB coloring
RGB coloring can be done using the (red, green, blue) syntax. Each parameter defines the intensity of a color between a range of 0 and 255. For example, an intense red can be given by the following property:
* {
color: rgb(255, 0, 0);
}Hex coloring
HEX coloring specifies an hexadecimal color with #RRGGBB, where the red, green and blue hexadecimal integers specify the components of the color, where ff is the highest value.
For example, an intense blue can be given by the following property:
* {
color: #0000ff
}HSL coloring
HSL coloring specifies the hue, saturation, and lightness of a color in the form (0-360,0-100,0-100).
For example, an intense green can be given by the following property:
* {
color: hsl(120, 100%, 50%)
}Formatting the background
We can use the background-color property to apply a background color to any element. If used for the <body> section, it applies to the background of the entire page.
The background-image is very similar, but it applies a background image instead of coloring it.
body {
background-color: blanchedalmond;
color:blueviolet;
/*background-image: url("doge.jpg");*/
}Box Model
CSS works with HTML wrapping elements with the CSS box model. It consists of content, padding, border, and margin.
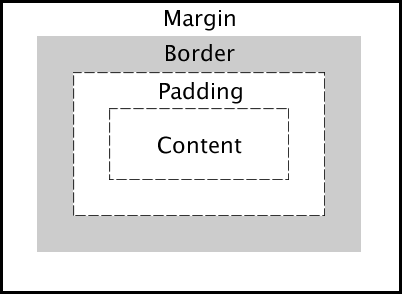
Then, you can specify each property and customize it. For example, you can use height and width as auto to let the browser calculate or specifying a value:
#heading {
height:100px;
width:250px;
background-color: chocolate;
}
#first-p {
width: 50%;
height: 200px;
background-color: blue
}
Borders
The borders can be customized using the border property, which is a shorthand for other properties like border-style, border-width and border-color. Using the shorthand, you can define all of them in a single declaration, or specify each border to apply to:
#heading {
border: ridge 5px cornflowerblue;
}
#first-p {
border-top: double red;
border-bottom: dotted pink;
border-left: solid blue;
border-right: ridge black;
}
Padding
The padding property sets the padding space on all sides of the element. the padding area is the space between the content and the border.
#heading { /* One value - all sides */
border: ridge 3px cornflowerblue;
padding: 50px;
}
#first-p {/* Two values - top/bottown left/right */
border: ridge 3px cornflowerblue;
padding: 50px 300px
}
#second-p {/* Three values - top left/right bottom */
border: ridge 3px cornflowerblue;
padding: 1px 150px 50px;
}
#third-p {/* Four values - top right bottom left */
border: ridge 3px cornflowerblue;
padding: 100px 100px 1px 100px
}
Margin
Margins create space around the element. You can use the margin property to specify margins.
#heading {
border: ridge 3px cornflowerblue;
padding: 50px;
margin:auto;
}
#first-p {
border: ridge 3px cornflowerblue;
padding: 50px 300px;
margin: 100px;
}
#second-p {
border: ridge 3px cornflowerblue;
padding: 1px 150px 50px;
margin: 50px 90px 10px;
}
#third-p {
border: ridge 3px cornflowerblue;
padding: 100px 100px 1px 100px;
margin: 10px 100px 500px 300px;
}