What is it?
Sampling is a statistical tool mainly used in Descriptive Statistics to select subjects from a study population, forming a sample.
The set of elements which will be studied a certain characteristic from is called population, which encompasses the entire dataset. In practice, it’s not viable to study the entire population, so statisticians opt to study just a subset of said population. This subset is called sample.
The difference between sample and population
Population refers to the entire data. Sample is any subset of the data.
Calculating sample size
Some factors can determine the optimal sample size, like the maximum error allowed, confidence of the study, and variance of the target variable.
For an infinite, parametric population, given as the Z-value corresponding to the confidence, as the estimated proportion, which can be estimated to if unknown, and as the margin of error:
Sampling techniques
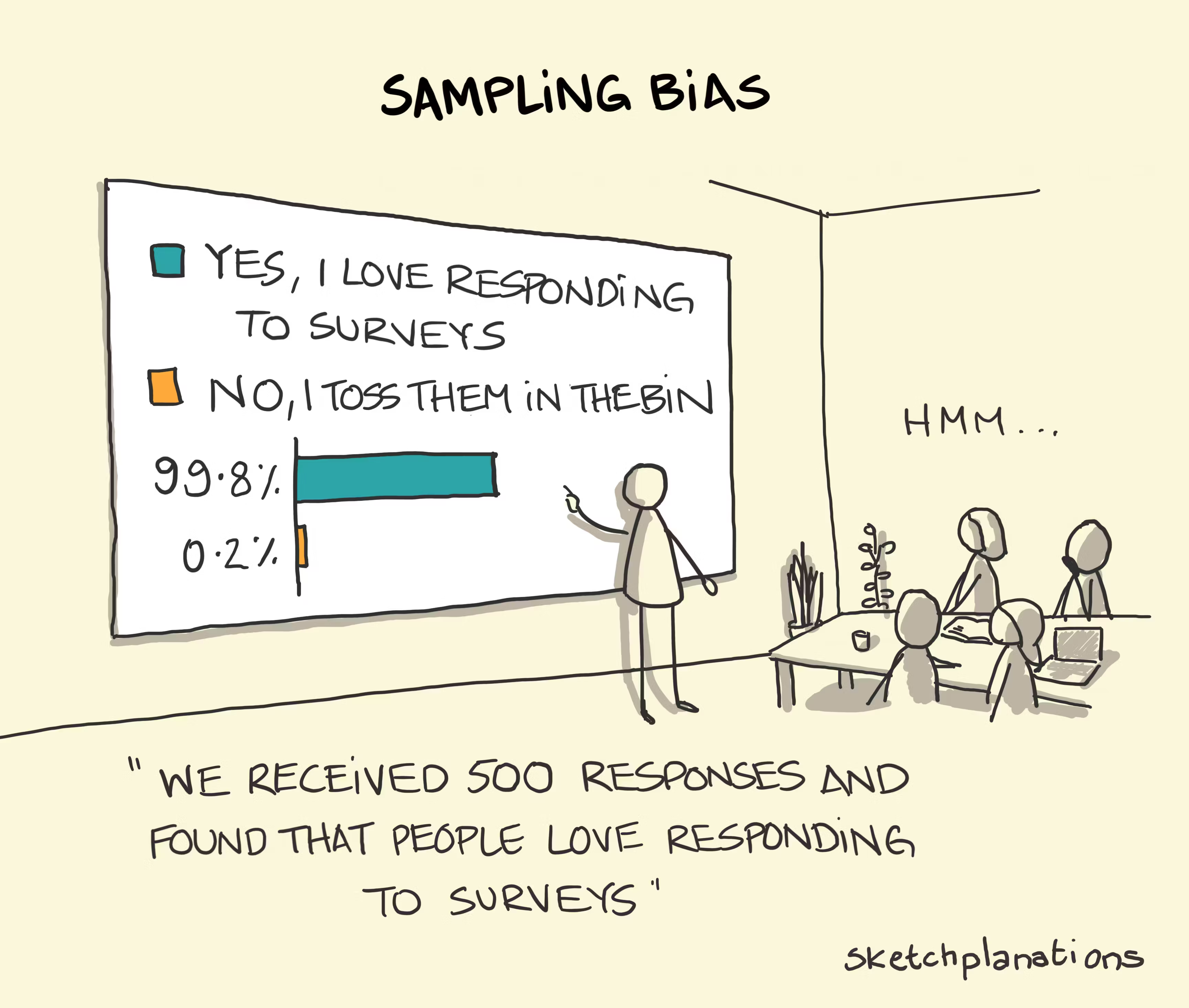
The process of extracting a sample from a population can yield bad samples that can add bias to the analysis. Because of it, we use sampling techniques to collect representative samples of the population.
Intentional sampling
Intentional sampling methods are non-randomized and non-probabilistic procedures, which results in a biased sample. The purpose of intentional sampling is to deliberately select a group of elements which satisfy specific prescribed criteria.
It should be used only with enough previous knowledge of the population.
When using intentional sampling, the study may lose its deterministic and probabilistic nature.
Simple random sampling
To perform a simple random sampling, each element from the population receives a number from to , and to collect a sample with size , draw random numbers corresponding to the elements, with or without reposition.
Should be used only with homogeneous and uniform populations.
Because each element can be drawn with equal probability, if the population is not uniform, it can add bias to the study.
You can easily perform a simple random sampling using Python:
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
"num_legs": [2, 4, 8, 0],
"num_wings": [2, 0, 0, 0],
"num_specimen_seen": [10, 2, 1, 8],
},
index=["falcon", "dog", "spider", "fish"],
)
series_sample = df["num_legs"].sample(n=3, random_state=42)
dataframe_sample = df.sample(frac=0.5, replace=True, random_state=42)Stratified sampling
In stratified sampling, the population is divided in more homogeneous sub-groups, called strata, in a way that the elements are homogeneous in the sub-groups and the groups are heterogeneous between other groups.
The way to draw samples from each strata differs from each type of sampling:
-
Uniform stratification
A simple random sampling is applied to each strata, drawing an equal number of elements from each strata.
-
Proportional stratification
A simple random sampling is applied to each strata, which the number of elements from each strata is proportional to the number of elements of the strata compared to the population.
-
Optimal stratification
Similar to proportional stratification, but now the Variance of the target variable is taken into consideration, measured by its Standard Deviation.