What is it?
A binary tree is a hierarchical Data Structure in which each node has at most two children, referred as left and right children. It’s widely used for storing, searching, and sorting data.
Each binary tree has three items, the data item, the address of the left child and the address of the right child.
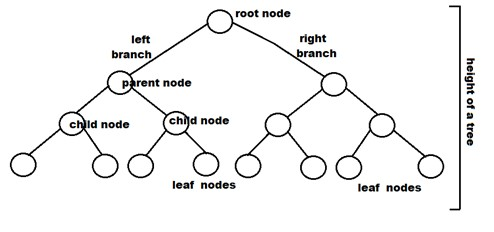
Characteristic of a binary tree
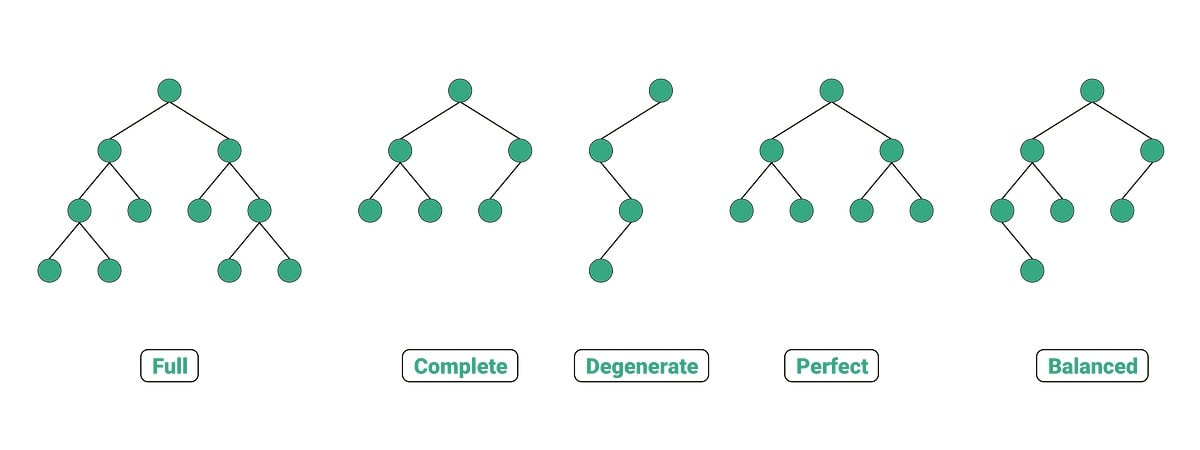
A binary tree can be classified as a full binary tree, perfect binary tree, degenerate binary tree, and skewed binary tree.
-
Full binary tree
A full binary tree happens when all nodes have or children. In other words, all nodes except leaf nodes have two children.
-
Perfect binary tree
A perfect binary tree is a tree where all internal nodes have children, and all leaf nodes are on the same level.
-
Degenerate binary tree
Also called pathological binary tree, it happens when every internal node has a single child. Performance-wise, it’s the same as a Linked Lists.
-
Skewed binary tree
The skewed binary tree is a degenerate binary tree which the tree is dominated only by left nodes or right nodes. Thus, it can be left skewed or right skewed.
Calculating elements at desired level
To calculate the number of elements of a binary tree, we use the height of the tree. The height is given by the difference of the root level, which is always equal to , and the desired element level.
We can get the maximum number of elements at a given level by using a simple rule. Given as the number of elements, and the depth of the tree, .