What is it?
Variables in Apache Airflow works like a normal Python variable. It reduces hard-coding and duplicate code. In Airflow, you can use the same variables in different DAGs and Tasks, and it works basically the same as XCOMs or Airflow Connections.
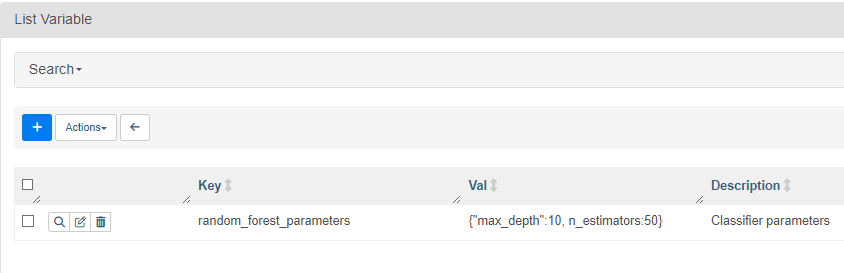
Variables have three components; key, value, and description. The key is the unique identifier, the value needs to be a serializable JSON, and the description helps to identify each variable.
Creating Variables
Variables are created inside the Web Server:

Resulting in:
Using Variables in DAGs
To be able to access the defined variables, the DAG needs to import airflow.models.Variable class. And to retrieve the value, just use the .get() method specifying the variable key and deserialize the JSON:
from airflow import DAG
from datetime import datetime
from airflow.models import Variable # To access the variables
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
def train_model(ml_parameter): # Receiving op_kwargs parameter
print(f"Training model with {ml_parameter}")
with DAG(
"variable_dag",
start_date=datetime(2024, 2, 25),
schedule_interval=None,
catchup=False,
) as dag:
# Connecting and retrieving defined variable.
max_depth = Variable.get(
"random_forest_parameters", deserialize_json=True)["max_depth"]
train = PythonOperator(
task_id=f"model_with_{max_depth}",
python_callable=train_model,
op_kwargs={"ml_parameter": max_depth}, # Passing as parameter
)
train